Engineering & Simulation
Where space meets engineering and modeling.
Explore the fundamentals of rocket engineering, spacecraft design, orbital mechanics, and physics simulation. Includes beginner guides to Ansys and other simulation tools used in modern aerospace engineering.
-
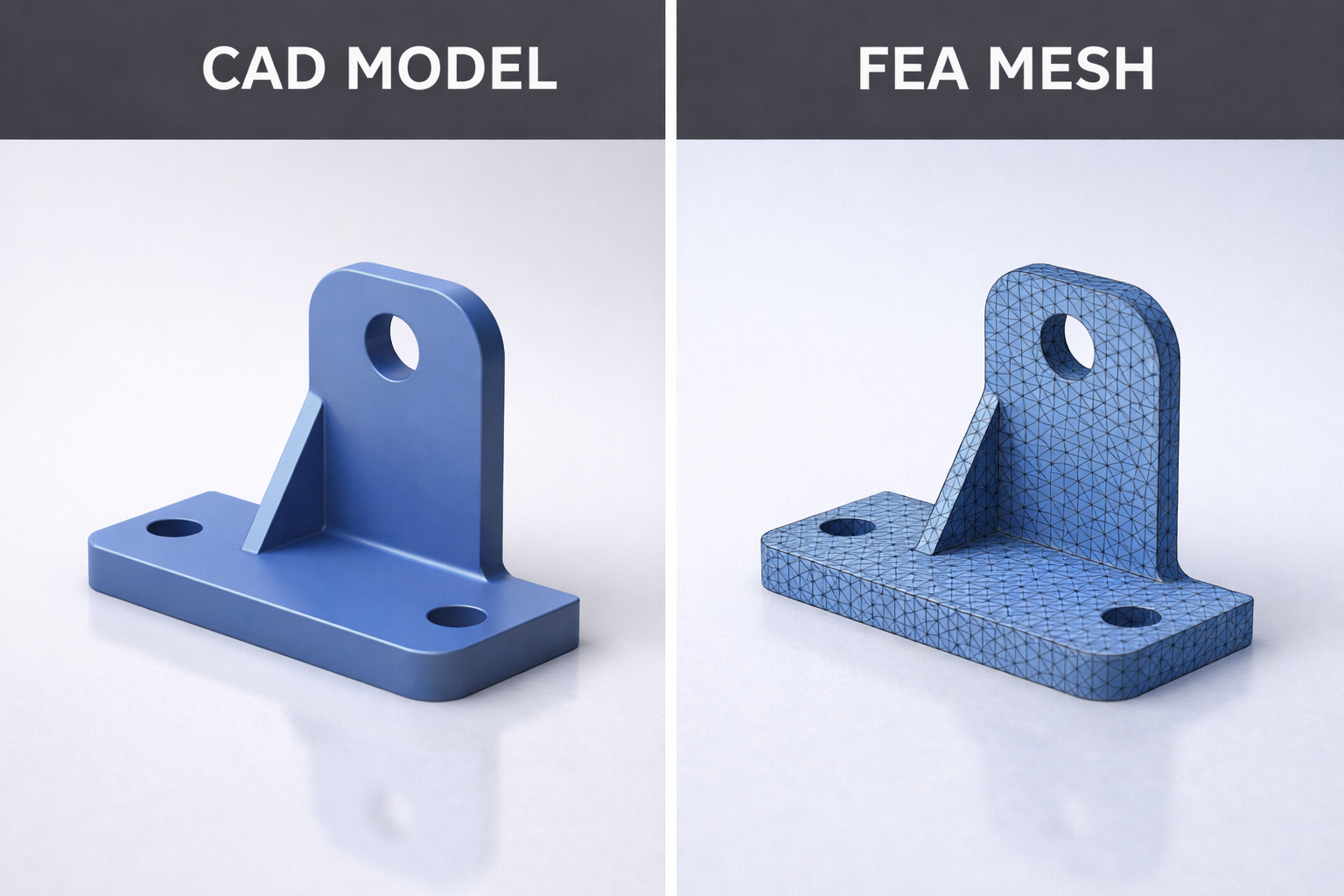
Basics of Finite Element Analysis Explained in Plain English
More Details: Basics of Finite Element Analysis Explained in Plain EnglishImagine you’re designing a bridge. Before spending millions of dollars building it, wouldn’t it be nice to know if it will hold up under heavy traffic? Or what happens during an earthquake? Or how it handles extreme temperatures? This is exactly what Finite Element Analysis does. It’s like having a crystal ball for engineers—except instead…
-
What Is a Physics Simulation? A Simple Guide for Beginners
More Details: What Is a Physics Simulation? A Simple Guide for BeginnersHave you ever watched a building crumble in a video game and thought, “Wow, that looks so real!”? Or maybe you’ve seen a movie where cars flip through the air in spectacular fashion? Here’s a secret: None of that is filmed in real life. It’s all thanks to something called physics simulation. Don’t worry if…
-
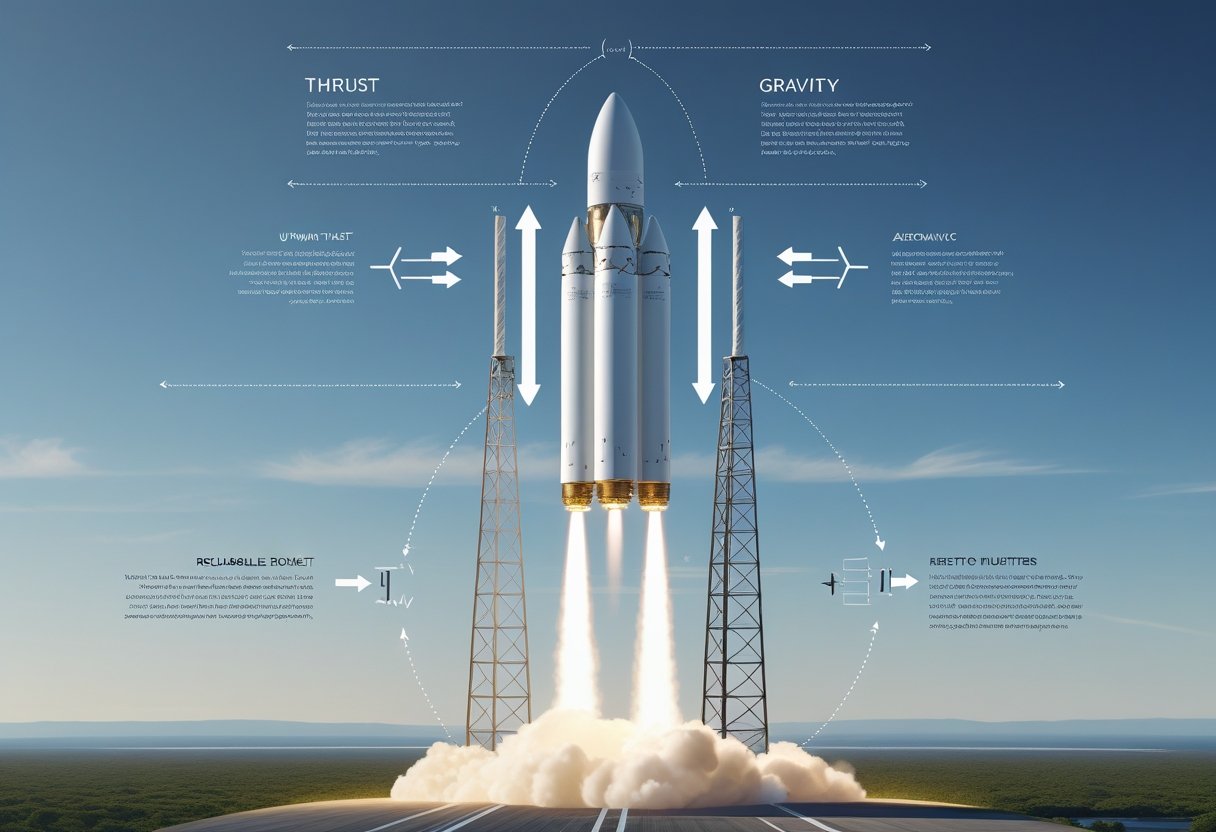
The Physics Behind Reusable Rockets (Explained Simply): Space Innovation Unlocked
More Details: The Physics Behind Reusable Rockets (Explained Simply): Space Innovation UnlockedYou’ve seen rockets land like slow-motion miracles, but you probably wonder how that works in plain physics. Reusable rockets save money and reduce space debris by bringing the most expensive parts back to Earth using controlled burns, aerodynamic steering, and precision landings. This article will break down the core forces, fuel trades, and engineering tricks…
-
How Engineers Design Space Rovers: A Simple Guide for Everyone
More Details: How Engineers Design Space Rovers: A Simple Guide for EveryoneYou’ll learn how engineers turn bold ideas into reliable machines that survive alien dirt, freezing nights, and months without real-time help from Earth. Engineers balance mission goals, harsh environments, and limited power to design rovers that move, sense, sample, and send back science—and this article breaks those choices down into clear, practical steps you can…
-
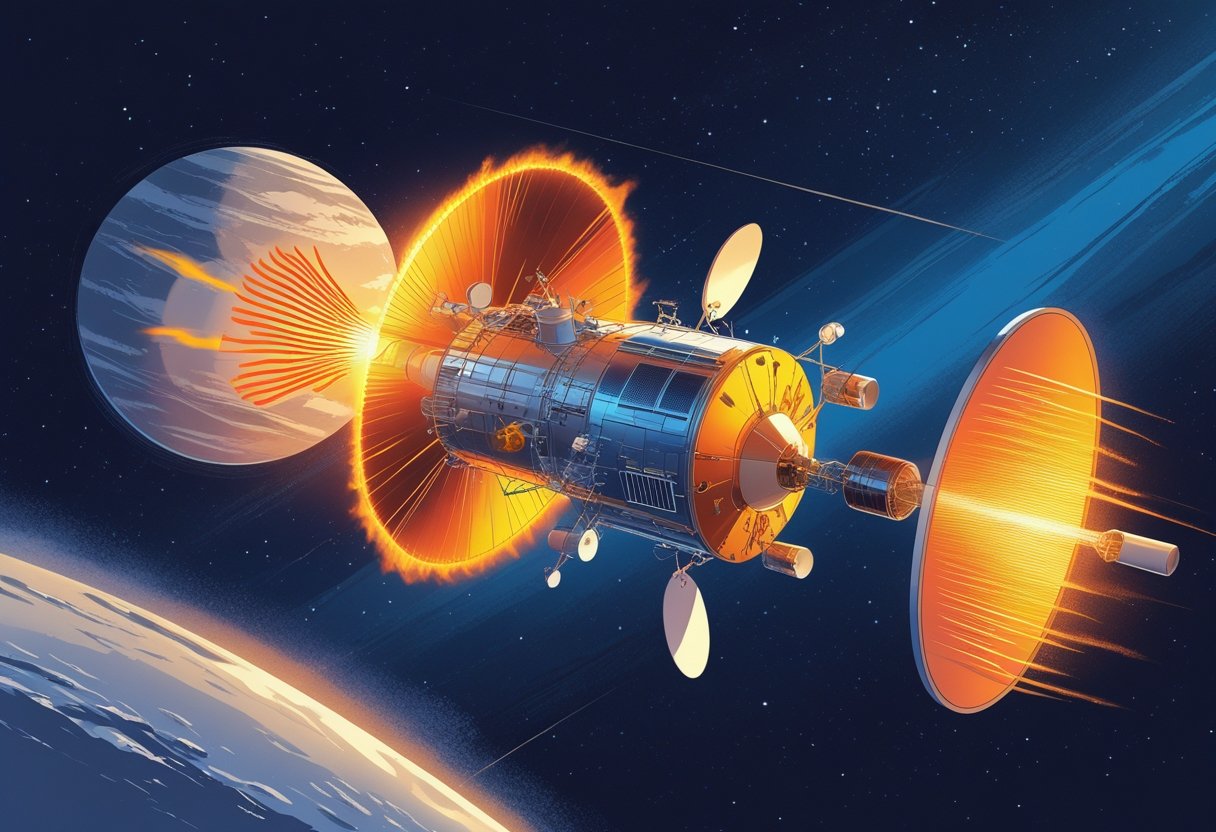
Lightweight Guide to Spacecraft Propulsion: Efficient Systems for Space Exploration
More Details: Lightweight Guide to Spacecraft Propulsion: Efficient Systems for Space ExplorationYou want a clear, compact introduction that helps you choose and compare propulsion options for any spacecraft mission. This guide gives you concise explanations of propulsion systems, the key metrics (thrust and specific impulse) that determine their trade-offs, and practical guidance to match engines to mission goals. Expect straightforward coverage of chemical and electric propulsion,…
-
How Solar Panels Work in Space: Harnessing Clean Power from Orbit
More Details: How Solar Panels Work in Space: Harnessing Clean Power from OrbitYou tap sunlight in empty space the same way solar panels do on Earth, but without atmosphere or nightfall the panels deliver more continuous, efficient power for satellites, stations, and probes. Solar arrays convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells, then power onboard systems or beam energy toward Earth for long-term missions. You’ll explore how…
-
How Spacecraft Survive Extreme Temperatures: Technologies and Tactics
More Details: How Spacecraft Survive Extreme Temperatures: Technologies and TacticsYou face extremes in space that would destroy ordinary machines: blistering heat near re‑entry or the Sun, and deep cold in shadowed regions or during lunar nights. Spacecraft survive these extremes by combining insulation, reflective coatings, regulated heaters, radiators, and fault‑tolerant electronics so systems stay within safe temperature limits. As you explore how engineers manage…
-
The Engineering Behind Telescopes (Simple Version): Exploring Light, Lenses, and Cosmic Wonders
More Details: The Engineering Behind Telescopes (Simple Version): Exploring Light, Lenses, and Cosmic WondersYou’ll find that telescope engineering balances simple physics with clever design so you can see faraway worlds. A telescope gathers and focuses light using lenses or mirrors, and engineers optimize size, shape, and materials so you get brighter, clearer views without bulky, fragile parts. This article walks you through how telescopes work, the main types…
-
Why Satellites Don’t Fall Out of Orbit: The Physics Explained
More Details: Why Satellites Don’t Fall Out of Orbit: The Physics ExplainedYou watch a tiny dot streak across the sky and wonder how it keeps circling without falling. Satellites stay aloft because their forward speed continuously bends their path around Earth, so gravity pulls them inward while their motion keeps them from hitting the ground. You’ll explore how gravity and motion work together, why different altitudes…
-
How Spacecraft Navigation Really Works: From Earth Orbit to Deep Space
More Details: How Spacecraft Navigation Really Works: From Earth Orbit to Deep SpaceYou control a machine that finds its place among moving planets and invisible forces, and this article shows how that happens. Spacecraft navigation combines precise ground tracking, onboard sensors like star trackers and gyroscopes, and timed radio links so missions hit targets across millions of kilometers. You’ll learn how those systems work together to plan…